Learn more
- Jun 27, 2008
Integrating Information Extraction into the KiWi-System: a proposal from Brno
Semantic technology isn’t about technology: It’s noble concern is to make the life and work of people easier. Yesterday, Marek Schmidt and Petr Knoth, both working on PhD project within Natural Language Processing (NLP) at Brno University, introduced their vision of how Information Extraction could be integrated into the KiWi-System.
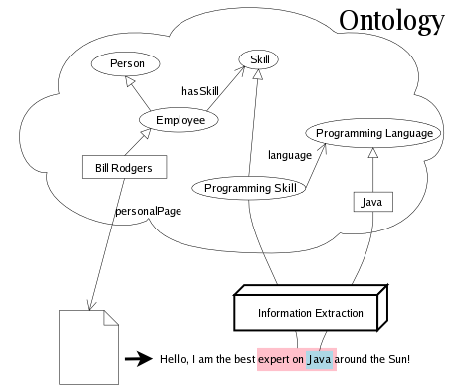
First off: What is Information Extraction? In natural language processing, “information extraction (IE) is a type of information retrieval whose goal is to automatically extract structured information, i.e. categorized and contextually and semantically well-defined data from a certain domain, from unstructured machine-readable documents” (Wikipedia). Marek and Petr’s vision for using IE in KiWi is to support the user in the creation of semantic annotations.
The image above illustrates their vision: If a user, for instance, enters the text “Hello, I am the best expert in Java around the Sun” into the content editor, structured information is extracted, analyzed on the fly and returned as suggestions. Through the application of reasoning on existing annotations and on further information that is available on the system – e.g. relevant domain ontologies, but also information about the user himself – the system will be able to infer new statements: E.g. the system will be able to infer that Bill Rodgers has Java programming skills, even though this information has never been explicitly stated in the knowledge base.